《超级社会:人类是如何在一万年来的战争中被塑造成地球上最伟大的合作者的》书评
Review of “Ultrasociety: How 10,000 Years of War Made Humans the Greatest Cooperators on Earth”
Professor Turchin’s new book Ultrasociety identifies the causal mechanisms hidden in the twists and turns of human civilisation by quantifying the rise and fall of empires. The book translates some of Turchin’s academic work on cliodynamics, making it accessible to the interested lay reader.
Turchin教授在他的新书《超级社会》中,通过对帝国兴衰的量化分析,来辨识出隐藏于曲折跌宕的人类文明史中的决定性机制。这本书深入浅出地阐述了Turchin教授在历史动力学领域的一些学术成果,让那些对此感兴趣的普通读者也能领会其中的奥妙。
What is cliodynamics? My best translation is that it is the scientific study of history that seeks to use quantification to test, eliminate and open new competing hypotheses about the evolution of human civilisation.
什么是历史动力学?我能给出的最佳定义是:这是一种研究历史的科学方法,它试图通过量化的方法去检验,排除和发掘关于人类文明演化的诸多相互竞争的假说。
Turchin draws the reader in with a puzzle. What social and psychological mechanisms give people the ability to contribute towards such enormous cooperative endeavours, like building the international space station? Turchin estimates that the total quantity of hours of human work and toil dedicated by the global workforce involved in the mammoth cooperative task of building the space station is around three-million people-years, or over 26 billion work hours.
Turchin教授提出了一个难题以吸引读者的兴趣:是哪些社会和心理机制让人们拥有了大规模协作的能力,完成了诸如建设国际空间站这样的宏伟目标呢?他估计全球劳动力投入在协作建设国际空间站这个庞大任务上的总人类工时大约是300万人年,也就是超过260亿工时。
The obvious next question is how this compares with the other great cooperative feats of history, like the 400,000 people-years required to build the Great Pyramid of Giza, or the 100,000 people years to build the Coliseum in Rome, and whether these long run patterns signal an increase in humanity’s ability to cooperate at a vast scale.
下一个容易想到的问题就是,这相比于人类历史上其它依靠协作完成的伟大工程又如何呢,例如需要花费40万人年修建的吉萨大金字塔,还有需要花费10万人年修建的罗马大竞技场,以及以上这些长期以来反复再现的模式,是否显示了人类在大规模协作能力上的进步呢?
As an economist my bias is to see human actions in terms of self-interest, competition and conflict, where through the invisible hand the interaction of self-interested individuals can lead to productive outcomes. But like the fish who is blind to the vast ocean of water they live in, I realised I was blind to the ocean of cooperation that was the back-drop to my focus on self-interest and competition.
作为一个经济学家,我倾向于通过自利、竞争和冲突的视角来看待人类行为,在这些视角之下,自利个体之间能够通过“看不见的手”达致有效率的经济产出。但就像大海里一条对于自己所生存的广阔水域一无所知的鱼一样,我意识我对于合作行为这片广阔的大海实际上几乎一无所知,而这是我所关注的自利和竞争的基础。
In “Ultrasociety” Turchin provides a way to see and measure cooperation – to quantify its existence on a massive scale. Once you are able to see the great ocean of cooperation that dominates human society, it leads you to interesting and challenging lines of scientific inquiry. The puzzling question is then how a world dominated by ultra social human cooperation can also frequently succumb to large scale war and conflict?
在《超级社会》一书中,Turchin教授提供了一种看待并衡量合作的方式——在大尺度上将它的存在进行量化。当你能够看清合作这片统治着人类社会的汪洋大海,它就会将你的引向有趣而又富有挑战性的科学探索。之后的一个问题就是:为什么一个充盈着超大型社会合作的人类世界还会经常屈就于大规模的战争和冲突?
Turchin’s answer, and one of the big ideas in the book, is that war between social groups is the mechanism by which cooperative behaviour develops “within groups”. It is a fundamental evolutionary process happening between societies at a large scale. He elevates war as a selection mechanism for cooperation, and values it above many of the technological factors like domestication of plants and the advent of agriculture.
Turchin对这个问题的答案,同时也是本书的主要观点之一,是认为社会群体之间的战争是合作行为在群体内部发展的机制。它是一种基础性进化过程,发生于在各社会之间的大尺度上。他提升了战争在历史进程中的地位,将其视为对合作行为的一种选择机制,并且将其价值置于许多技术性因素之上,例如植物的驯化和农业的出现。
Turchin debunks many standard stories that “explain” the path to civilisation and eliminates glaring inconsistencies in the archaeological record. The naive view that the invention of agriculture “…set the ball rolling, and the entire history of civilisation followed from that” is a satisfying common story. But it seems a stretch to claim that the small scale practice of seasonally collecting and planting seeds nearby small permanent settlements, leads directly to the large-scale institutions observed in ancient civilisations.
Turchin推翻了许多自称能够“解释”通向文明路径的标准叙事,认为它们忽视了自身与显而易见的考古学事实之间的重大矛盾。有一种天真的观点认为,农业的发明“……让雪球滚动了起来,而整个文明的历史则随之展开”,这是一种令很多人满意的常见叙事。但是,认为小规模永久定居点附近季节性的收集和播种行为可以直接导致古代文明中所呈现的一些大规模社会制度,这似乎有点太过牵强了。
The “agricultural snowball” story is also hampered by the fact that early agricultural societies had “a markedly negative effect on human health” as the poorer nutrition compared to hunter gatherers lead to smaller stature, higher sickness and the spread of pathogens through the high density settlements. Yet agriculture did spread and ultimately outcompeted nomadic hunter-gather societies.
早期的农业社会“对人类的健康水平产生了显著的负面影响”这一事实也削弱了“农业的雪球”这一叙事的说服力,相比于狩猎-采集社会,农业社会更差的营养水平导致了更小的体形,更多疾病,以及高密度的聚居区内病原体的传播。尽管如此,农业社会的确在之后得到了扩张并最终超过了游动性的狩猎-采集社会。
I have long been hesitant about “just so” explanations of social institutions based on historic physical and technological conditions that turn simple correlations into plausible causal mechanisms. Turchin provides the evidence that although all early large scale civilisations had agriculture, it was not the agriculture alone that directly caused large scale civilisation.
这种对于社会制度“原来如此”解释【编注:『原来如此故事』又称特例假设(ad hoc hypothesis),是一种为某一解释设置无法或难以验证的特殊条件,从而消除或降低该解释之可证伪性的做法。】,立足于物质和技术方面的历史条件,把简单的相关性当成了煞有其事的因果关系,我因此而一直对此抱有怀疑态度。Turchin教授提供了证据以显示虽然所有早期的大型文明都拥有农业,但并不是农业这一单一因素直接导致了大型文明的出现。
I felt foolish to have not recognised the array of “just so” stories in the study of history before Turchin pointed them out. In my field of economics, the existence of money is still explained in the textbooks as arising automatically once someone in human prehistory realised that some kind of currency made commerce easier than trying to directly trade a quarter of a cow for three baskets of vegetables.
对于没能在Turchin教授指出之前认出这些“原来如此”故事,我感到自己有点傻。在我所研究的经济学领域中,货币的存在仍然在教科书中被解释为在史前时代的某个时刻有当人意识到某种形式的通货比直接使用四分之一头牛去交换三筐蔬菜变得更加容易的时候自动产生的。
Yet many alternative social arrangements also solve the physical problem of a “double coincidence of wants”. We need look no further than current tribal societies that do not have or desire money despite their specialisation into many roles. They have instead resolved their double coincidence of wants dilemma through various other rituals, hierarchies, and institutions.
然而,许多其他的社会安排也同样解决了“双方需求的巧合匹配”这个实际问题。我们只需要看看一些现存的部落社会,虽然这些社会中已经出现了众多专业化的分工角色,但他们至今既没有货币,也看不出对货币有任何需求。取而代之的是,这些部落社会通过多种仪式,层级结构和社会制度的安排解决了“双方需求的巧合匹配”这一困境。
Turchin, through his cliodynamics research agenda, aims to rid the historical study of civilisation from these “just so” explanations. In the aim of scientific progress this research agenda uses quantifiable historical data to pit multi-level selection theory and its various components against many others, and in doing so eliminate bad theories and open up new avenues of inquiry. Most chapters of the books contain references to this emerging field of research which themselves are intriguing and enlightening.
Turchin教授希望通过他的历史动力学使文明史的研究摆脱这些“原来如此”解释。为了推进研究的科学化进程,他的研究里使用了可量化的历史数据让多层次选择理论以及它的不同组成部分与众多其它的理论进行竞争,通过这种做法排除那些较差的理论并为之后的研究打开新方向。书中的大多数章节都包含了对这一蓬勃发展的研究领域的描述,而这本身已经足够有趣和富有启发性了。
Turchin argues that human societies, tribes, and groups, did not simply take a linear path from small hunter-gatherers tribes to large-scale civilisations. It was the competition through conquest and war between societies that lead to those with more effective weaponry and military organisations arising from greater internal cooperation, to survive at the expense of others.
Turchin认为,人类社会,部落和群体并不是简单地通过一条线性的道路从小规模的狩猎-采集部落发展为大型文明的。不同社会之间在相互征服和战争中所展开的竞争,使得那些通过更好的内部合作发展出了更高效的武器和军事组织的社会生存了下来,而代价则是其对手的消亡。
The following excerpt summarises:
以下引文对此作了总结:
“Here’s how I think these peaceful, stable societies came about. As war created large states, empires, and nation-states, societies evolved measures to suppress internal conflict and violence. Reduced internal violence is the obverse of increased cooperation.
“我认为这些和平而稳定的社会是以这样的方式诞生的。随着战争创造出大型的城邦,帝国和民族国家,社会也演化出了一些压制自身内部的冲突和暴力的机制。内部暴力行为减少的另一面是更多的内部合作。
“Surprising as it may seem, the trend towards greater peace was already noticeable during the Ancient and Medieval historical eras, long before the Enlightenment of the 18th century. Of course, wars between empires dwarfed intertribal conflicts in scale. Huge armies fought increasingly bloody battles, and the numbers of casualties mounted.
“也许看起来让人吃惊,但向更加和平的状态演化的趋势,实际上在古代和中世纪这些历史时期中就已经显而易见了,这要远远早于18世纪的启蒙运动。当然,帝国之间的战争在规模上让部落间冲突相形见绌。大型军队间战争的血腥程度持续上升,而战争中的伤亡人数也随之水涨船高。
“But the key point is that these wars moved away from imperial centers, towards the frontiers. More and more people—those living far from frontiers where battles were fought—never experienced conflict, and could enjoy relative prosperity.
“但关键在于这些战争不再发生于帝国的中心区域,而被移到了前线。越来越多的人——那些生活在远离战争发生的前线地区的人——从来没有经历过冲突,他们享受到了相对的繁荣。
“There is no contradiction between larger armies and larger butcher’s bills from warfare, on the one hand, and on the other, a greater part of the population enjoying peace. What is important from the point of view of quality of life is not how many people, in total, are killed, but what the chances are that I (or you, or someone you care about) will be killed. In other words, the important statistic is the risk of violent death for each person.”
“一方面,军队规模更大,战争的死亡人数更高,而另一方面,总人口中更大比例的人群却能够享受和平,这两点并不冲突。从生活质量的角度来看,重要的并不是总体上有多少人在战争中被杀死,而是作为社会中的个体,我(或者是你,或者是你所关心的人)有多大的可能被杀死。换句话说,对每个人而言,更重要的统计量是死于暴力的风险大小。”
The power of this view is in the way the apparent contradiction of how war leads to peace becomes obvious once understood through an evolutionary lens. It changed my mental model of history from a series of inevitable linear events, to one of a branching tree of evolutionary paths, complete with many dead-ends of failed civilisations and their cultures, with many more merging and growing from conquest.
这一观点的强大之处在于,“战争是如何导向和平的?”这一看似矛盾的问题一旦通过进化的视角来理解,其中的逻辑就显而易见了。它将我理解历史的心智模型从一系列不可避免的线性事件的串联转变为一棵包含多种进化路径的分叉树,这棵树的许多分支都终结于失败的文明及其文化,但更多的分支则是通过征服合并在一起并继续成长的文明。
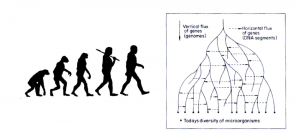
In short, I have shifted away from the popular but incorrect view of evolution as linear and subject only to environmental stresses rather than intra-species conflict. The left panel of the below image epitomises this popular confusion that I ignorantly held in the context of the study of history.
简而言之,我已经摒弃了那种流行却是错误的以线性视角看待文明演化的方式,该方式认为它仅仅受到外部环境的压力影响而不理会种群内部冲突的作用。下图左边的部分代表了之前的我出于无知而在历史研究中所采用的这种带有很强迷惑性的流行视角。
A more correct view of biological evolution is in the right panel, complete with mixing of genes and extinctions. It is more subtle and complex view, but provides a more useful story of the path of history, the dying out of civilisations and merging of cultures as a result of inter-group warfare.
而下图中右边的部分则代表了一种更加准确的看待生物进化的视角,进化是在众多基因的混合与消亡中完成的。这是一种更加精细也更加复杂的视角,但它提供了一种对历史路径更加有用的叙事,文明的消亡和文化的合并实际上是族群间战争的结果。
Even more interesting is that when there is little external warfare and competition, the successful groups find it difficult to curtail infighting amongst sub-groups within their society, and their lack of internal cooperation begins to make them vulnerable to attack from outsiders. In Turchin’s own words, from Chapter 2:
更有趣的是,当来自外部的战争和竞争压力较小时,那些成功的族群会发现控制自身内部小群体间的明争暗斗变得更困难了,而缺乏内部合作将会让这些曾经成功的族群在面对外来者的攻击时变得脆弱。用Turchin在书中第二章的话来说就是:
“Here’s how war serves to weed out societies that “go bad.” When discipline, imposed by the need to survive conflict, gets relaxed, societies lose their ability to cooperate. A reactionary catchphrase of the 1970s used to go, “what this generation needs is a war,” a deplorable sentiment but one that in terms of cultural evolution might sometimes have a germ of cold logic.
“战争是以这样的方式淘汰掉那些“衰朽腐败”的社会的。当因生存压力而施加的纪律开始变得松弛的时候,社会就失去了合作的能力。1970年代曾经有一句反动标语,“这代人需要经历一场战争,”虽然这句话里满是可悲的情绪,但从文明进化的角度上说,也许其中的确包含着一些冷冰冰的真知灼见。
At any rate, there is a pattern that we see recurring throughout history, when a successful empire expands its borders so far that it becomes the biggest kid on the block. When survival is no longer at stake, selfish elites and other special interest groups capture the political agenda. The spirit that “we are all in the same boat” disappears and is replaced by a “winner take all” mentality. As the elites enrich themselves, the rest of the population is increasingly impoverished. Rampant inequality of wealth further corrodes cooperation.
无论如何,我们都能看到历史中不断重演的一种模式,当一个成功的帝国将自己的疆域扩展得如此之广以至于它成了“街区里的孩子王”,当生存的压力已不再迫在眉睫,那些自私的精英和其它一些特定的利益集团就会夺取帝国的政治议程。“大家同处一条船”的精神消失了,取而代之的是“赢者通吃”的心态。随着精英们发家致富,其它人则持续地变得更加贫困。肆无忌惮的贫富不均进一步腐蚀了合作的基础。
Beyond a certain point a formerly great empire becomes so dysfunctional that smaller, more cohesive neighbors begin tearing it apart. Eventually the capacity for cooperation declines to such a low level that barbarians can strike at the very heart of the empire without encountering significant resistance.
在超过一个临界点之后,一个曾经的伟大帝国就会变得机能失调,以至于它的那些更小但更具凝聚力的邻居们开始将它分裂。最终帝国内部的合作能力降到了一个太低的水平,以至于外来的野蛮人可以在几乎遇不上任何值得一提的抵抗的条件下直捣帝国的心脏。
But barbarians at the gate are not the real cause of imperial collapse. They are a consequence of the failure to sustain social cooperation. As the British historian Arnold Toynbee said, great civilisations are not murdered – they die by suicide.”
但那些“门口的野蛮人”并不是帝国崩溃的原因。他们的入侵只是帝国没能维持内部社会合作的结果。正如英国历史学家阿诺德·汤因比所言,伟大的文明从来不会被谋杀——他们全都死于自杀。”
I have explored this process of disintegration of groups into competing clans in small scale in experiments before. Yet I failed to see the link to the large scale selection processes occurring even at such large scales at the nation-state. The talk of sclerosis and the death of large scale cooperation made me recall the chart below on the growth of partisan policy in the US which shows the striking decline in cross-party cooperation on legislative changes.
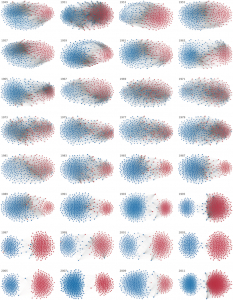
我之前曾经用小规模实验的方式研究过族群瓦解为多个相互竞争的部落的情况。但我并没有意识到,即使在民族国家这么大的尺度上,也有类似的选择过程发生。书中关于社会固化和大规模合作的消亡的讨论,让我联想起了下面这幅关于美国党派政策演化的图中所显示出在立法变更上的党际合作水平的显著下降。
Each node in the visual is a member of the U.S. House of Representatives from 1949–2012, with Republicans in red and Democrats in blue. Edges are drawn between members who agree on legislative decisions more often than expected by chance, and the nodes are spaced out in a way so that those with more edges connecting them are closer together. The clustering therefore visualises who is cooperating with who in terms of developing legislation.
图中每个节点都代表美国在1949-2012年间的一位众议院议员,红色代表共和党人,而蓝色则代表民主党人。如果两位议员在立法决策上达成一致的频率高于由随机概率所预期的水平,那么他们所对应的节点之间就会被一条线连接,节点在图中的排列方式使得那些相互之间有更多连接的议员靠得更近。这样图中的聚类就从视觉上反映出了哪些议员在推进立法上相互合作。
Without the external threats to the nation as a whole after WWII, and later the Cold War, the ability to maintain a cohesive national whole in political terms appears to have broken down into partisan scrambling. No longer can we see a cooperative whole, but instead competing fairly arbitrary tribes of blues and reds.
在第二次世界大战和随后的冷战结束后,来自外部的对于美国作为一个整体的威胁都不复存在了,而从政治角度上看,似乎维系一个有凝聚力的国家整体的能力也随之分崩离析,取而代之的则是喋喋不休的党派纷争。在图中我们不再能看到一个富有合作性的整体,而是一些分别由红点和蓝点组成的武断分隔的竞争部落。
I was left in a state of deep reflection after reading the book. Many other big ideas are woven through it to make you reconsider the popular but overly simplistic stories we tell ourselves to explain historical events. From the long term Z-shaped arc of quantifiable violence in human civilisation, to the role of horses, long range weaponry and population size in the success of inter-group warfare, and finally to the rise of God-kings and oppressive hierarchies.
在读完这本书后,我陷入了深刻的反思。本书中还贯穿了许多其它重要想法,它们会让你重新思考我们在解释历史事件时所常用的那些流行但过分简化的叙事。从人类文明中以可量化方式衡量的暴力水平在长期中所呈现出的Z型曲线,到马、远程武器和人口规模在族群间战争中所发挥的作用,以及最后君神合一政体和统治阶级的崛起。
Even Turchin’s incidental detours explore rather significant questions, such as in Chapter 4 when he clarifies a point about culture in human societies with the off-handed comment “Incidentally, why do we have culture? ”
即使是Turchin教授在书中偶然从主线上岔出的一些分支也讨论了相当重要的问题,例如在第四章中澄清关于人类社会中文化的作用的一个观点时,他随性地评论道“顺便问一句,为什么人类会拥有文化?”。
The same lesson applies in economics. Firms in highly competitive markets constantly face threats to their existence, leading to a type of destructive creation that ensures that surviving firms are internally highly cohesive and cooperative; economically efficient.
同样的道理也适用于经济学领域。高度竞争市场中的企业经常会面临威胁到自身生存的问题,这导致了一种毁灭性的创造过程以保证最终生存下来的企业在内部都具有极强的凝聚力和合作能力,我们称之为经济效率。
Yet the process of competition is highly inefficient in economic terms as only very slightly different production facilities are duplicated by competitors. For me the trade-off is rather radical just to think about. That the gains to internal cohesion require a cost of an external threat or else large-scale groups will be undermined by the interests of sub-groups within them.
然而从经济角度上说,竞争本身是非常低效的,因为众多互相竞争的对手所复制的生产设备之间的差别其实非常小。对我来说,其中的利弊权衡已经是一个相当深刻的问题了。即获得内部凝聚力所带来的收益需要以面对外部威胁为代价,否则大规模的群体将会被内部众多小团体的利益慢慢腐蚀。
Like any books that cover grand ideas about human civilisation there are probably some finer details to squabble about. I certainly don’t have the expertise to do so. Instead I want to share some of the thoughts that occupied my mind after reading Ultrasociety. These thoughts and comments should sufficiently signal the compelling nature of the discussions and ideas of the book.
与任何涉及关于人类文明的宏大观点的著作一样,书中几乎肯定会有一些值得争论的细节。我显然不具备足够的专业水平来这么做。但我希望与各位分享在读完《超级社会》这本书之后一直占据我脑海的一些想法。这些想法和评论应该足够说明这部大作的引人入胜之处以及其中的一些主题。
First, if sustained group cooperation relies on external competition, is there value in creating fictitious interstellar enemies to sustain better global cooperation? I’m thinking here of the film The Village, where the elders invented an outside enemy to sustain internal peace. The idea of creating an enemy for solidarity is popular, and even gets a run in the economics comics.
首先,如果持续的群体合作依赖于外部竞争,那么创造一些假想中的外星敌人是否对于维持更好的全球合作具有价值呢?这让我想起了一部名为《神秘村》的电影,在这部电影中,老人们创造出了一个外部敌人来维持村子内部的和平。为了维持团结而创造出一个敌人的想法现在很流行,即使在一些经济学漫画中也能看到它的影子。
Or perhaps the major modern religions fulfil this type of role so well that they can’t be displaced[1]? And surely it is the moral thing to do to promote human cooperation on an even larger scale without actual conflict and violence, if that indeed is possible.
或者也许主要的现代宗教已经扮演了这一角色而因此变得无可取代[1]? 毫无疑问,在不引发实际的冲突和暴力的前提下推进更大规模的人类合作在道德上是无可厚非的,如果这真的可能的话。
Second, and following directly on from the first, the use of the term morality is widely used with its common meaning as conforming to the cooperative norms of a group. Yet I can’t shake the nagging feeling that, like Darwin’s work on evolution, the idea that war with outsiders promotes peace is ripe to be corrupted for political gain because it can be so easily argued to be a ‘natural’ or ‘moral’ position.
第二,紧跟第一点的思路,现在人们对于“道德”的惯常理解与维持社会的合作规范是一致的。然而我还是无法摆脱一种令人不安的感觉,正如达尔文在进化论上的贡献一样,认为与外来者的战争能够推进内部和平这一观点很容易被政治利益所利用,因为它很容易被说成是一种“自然的”或是“道德的”立场。
Third, how are these great feats of cooperation realised in practice? Is there a common recipe that can be adopted into 21st public policy? There is a brief mention of how tribes and groups ‘tag’ each other with signals of group membership as one way to create cooperation in the following passage from Chapter 10.
第三,这些宏大的合作是如何在实践中实现的?对于21世纪的公共政策而言,存在一种通用的实践模式吗?书中第十章的以下段落简要地提到了部落和群体是如何用“标签”来标识彼此群体身份的方式来创造合作的。
“An important evolutionary breakthrough was the capacity to tag cooperating groups with symbolic markers such as language and dialect, styles of clothing and ornamentation (including tattoos), and behavioral characteristics—for example, participation in collective rituals. Symbolically-tagged cooperative groups, or tribes and nations, allowed us to increase the scale of cooperation beyond the circle of people personally known to us. Of course, the downside of increasing cooperation within a tribe or a nation was greater intensity of conflict with other tribes and nations.”
“一个进化上的重大突破就是人们通过诸如语言和方言,衣着和装饰(包括纹身)的风格,以及行为特征——举例来说,对于集体仪式的参与——这些符号化的标记来为与自己合作的群体贴上标签的能力。通过符号化标签来标记与自己合作的群体,或者部落和国家,让我们能够在熟人小圈子之外扩大合作的规模。当然,在部落或国家内部增进合作的负面效应是与其它部落和国家之间冲突强度的加剧。”
But like many of the minor points in the book, this single paragraph opens, then closes, a massively interesting puzzle about how humans actually organise into tribes at all levels. While as outsiders we easily observe tags, or the signals and rituals of a cultural group, as insiders we often overlook the amount of resources devoted to these tagging rituals.
但与书中其它一些次要观点一样,书中的这个段落首先提出了一个重要而有趣的难题,也就是人类是如何在实际中被组织为各种层次的“部落”的,并在之后回答了这个问题。作为外人,我们很容易观察到一个文化群体的标签,或者信号和仪式,但作为群体内部的人,我们却通常会忽视投入到这些标记仪式上的大量资源。
The whole fashion industry is almost exclusively about signalling social status, religious, sporting, or gender loyalties. People don’t buy cars just for transport; otherwise there would be little demand for more than a few different models.
整个时尚产业的存在几乎就是为了标识人们的社会地位,宗教信仰,体育爱好或性别取向。人们买车的目的并不仅仅是为了交通,否则除了有限的几种不同车型之外,不会有多少对其它车型的需求。
Instead we buy into marketing messages about how purchasing different types of cars tag us with different traits in the minds of others. At a national sale with have flags, anthems, national colours, sports teams and more that promote a sense of belonging.
但实际上人们买车也是在购买一种营销符号——通过对不同车型的选择而为自己贴上标签——你开的车显示出你是什么样的人。而国家则通过国旗,国歌,国家的代表性颜色,各种体育项目的国家队以及诸如此类的东西来让人们产生认同感。
While I’ve always considered much of our conspicuous consumption to be wasteful, in the same way that the devotion of military resources often appears wasteful on the surface, a picture is emerging of the amazing gains from these types of tagging behaviours and rituals in terms of promoting high levels of cooperation. While not the direct focus of the book, I think more details on this part of the evolutionary view of cooperation and conflict would have been valuable.
虽然我之前一直认为大多数炫耀性消费都很浪费,正如我们投入在军事上的资源通常从表面上看来都很浪费一样,但一幅由这类“贴标签”的行为和仪式通过在更高层次上提升合作水平而带来巨大收益的图景正在我的脑海中浮现。虽然这并不是本书直接关注的内容,但我认为,就有关合作和冲突的进化观点的这一侧面挖掘更多细节将是非常有价值的。
Fourth, what role does the massive advance in long-range weaponry since the dawn of the nuclear age mean for inter-group warfare? Turchin explains vividly how technology that allows for killing enemy combatants from a distance was a recipe for success in most warfare; starting with our evolved physical ability to accurately throwing rocks and spears, to the invention of bows and arrows, to the use of horses to mobilise armies over great distances. In the age of intercontinental missiles, drones, and nuclear weapons, how does the function of long-range of weaponry play out when the whole world can be anyone’s target?
第四,自从核武时代以来,远程武器技术的巨大进步将在群体间战争中扮演怎样的角色?Turchin教授在书中生动地描述了为什么那些能够在远程杀死敌军战士的技术在大多数战争中都是制胜的法宝,从早期人类演化出的准确投掷石块和长矛的能力,到弓和箭的发明,到使用马匹来让军队获得远程的机动性。在这个洲际导弹,无人机和核武器的时代,当整个世界都可以成为任何人的打击目标,远程武器又将如何发挥其作用?
Fifth, if the cooperative effort required to wage large scale war is a major part of the causal story of the history of civilisation, how significant is the legacy of previous wars in the current economic landscape? I have in mind the major industries of modern society, such as passenger airlines arising from industrial investment in aerial warfare, and the digital age legacy of military investment in remote communications.
第五,如果合作的努力是为大规模战争服务的这一因果叙事的确占据了大部分的文明史,那么之前的战争所留下的遗产在当今经济版图中又有着怎样的重要性?我所能想到的现代社会的一些重要产业,例如客运航空业,就是从对空中战争的产业投资中崛起的,而当今的数码时代也起源于军工行业对远程通信技术的投资。
Most major industrial firms of the modern age were intricately involved as military suppliers or were privatised former military organisations. Many modern cities only exist because of the strategic benefits of their local military bases, while public major works such as highway and rail systems, ports and airports, were products of military strategy more than peaceful economic investment.
现代大多数主要工业企业都曾经以各种复杂的方式扮演过军队供应商的角色,或者本身就是由之前的军工组织私有化而来。许多现代城市存在的原因就是处于当地的军事基地所带来的战略性优势,而高速公路,铁路系统,港口和机场这类重大的基础设施则更多都是军事战略的产物,而非和平时期经济投资的产物。
And, surprisingly to me, the cooperative legacy of previous wars is not simply technological, but also institutional; from the organisational structures of firms, to the welfare state, to international treaties on money and trade. The employer-worker relationship looks a lot like the soldier-army relationship, requiring induction, uniforms, codes of conduct, and hierarchal rule.
让我感到意外的是,之前的战争所带来的合作遗产并不仅仅存在于技术方面,它同样存在于组织制度中,从现代公司的组织结构,到福利国家,到国际货币和贸易条约。雇主和工人的关系看起来很像军队与士兵的关系,两者都要求正式入职程序,统一制服,行为准则以及层级化管理。
Modern provisions of the welfare state, including housing, health services and cash payments, were often originally created for returned soldiers following wars. It is no leap to suggest that our international monetary system, and the various international organisations and treaties that accompany it, is the direct result of resolutions in the shadow of the WWII. And perhaps the apparent breakdown of the social equality nurtured by post-war institutions observed since the late 1970s in many western countries is merely there result of the absence of external threats which breed infighting and abuses of power.
当代福利国家提供的各种供应品,包括住房,医疗服务和现金支付,最初通常都是在战后提供给退役士兵的。当今的国际货币体系以及与之配套的各种国际组织和条约,都是在第二次世界大战的阴影之下所达成的一系列决议的直接后果,这并不是什么新鲜的观点。而也许从1970年代晚期开始,许多西方国家中由战后建立的机构所导致的社会平等局面的崩塌,也仅仅是因为外部威胁的缺失为它们提供了内部斗争和权力滥用的温床。
As you can see, “Ultrasociety” will leave you pondering many big questions you may never have thought to ask before. I certainly see the world differently now. And that, to me, is the sign of a profound and insightful work.
正如你所看到的,《超级社会》这本书将会让你去深思一些之前不曾想到过的大问题。在读完这本书后,我眼中的世界变得明显不同了。对我来说,这意味着我读到了一部意义深远而富有洞见的大作。
尾注:
Turchin cites Ara Norenzayan’s book Big Gods: How Religion Transformed Cooperation and Conflict when explaining the role of religion in large scale cooperation, and I recommend reading it as well.
在解释宗教在大规模合作中所扮演的角色时,Turchin引用了Ara Norenzayan的著作《大神:宗教是如何改变合作与冲突的》一书中的内容,我也推荐读者阅读这本书。
翻译:Veidt(@Veidt)
校对:小聂(@PuppetMaster)
编辑:辉格@whigzhou